Key Takeaways
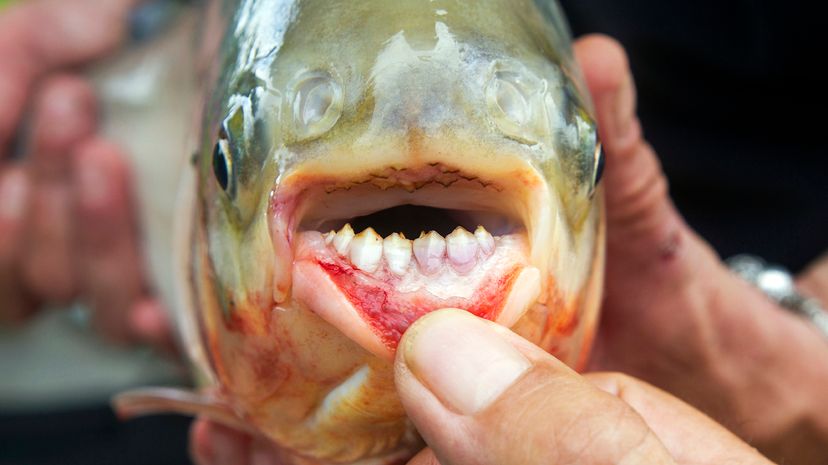
- Pacu fish, native to South America, are known for their humanlike teeth and can grow up to 3 feet (0.9 meters) in length.
- They are primarily herbivores — feeding on fruits, nuts and plant material — but can occasionally eat small fish and invertebrates.
- While generally not dangerous to humans, pacus can disrupt local ecosystems when introduced to non-native environments.
In 2023, 11-year-old Charlie Clinton from Oklahoma made headlines by catching a pacu — a South American fish known for its human-like teeth — in a pond behind his house, far from its native Amazon habitat.
The pacu fish was released back into the pond under the local catch-and-release guidelines before the Clintons realized its potential impact on the ecosystem. The Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation has since highlighted the ecological risks of releasing non-native species into local habitats. They advise anyone who catches a pacu to keep it to prevent disruption to local wildlife.
Advertisement
This rare occurrence of a South American species in Oklahoma waters has drawn attention to the broader issue of invasive species and their effects on ecosystems. But what exactly do we know about this fish, and just how dangerous is it to non-native habitats?
Advertisement